Refraction of Light
The Concept of Refraction of Light
Explain the concept of refraction of light
Refraction of light refers tothe bending of light as it passes through two different medium because the speed of light tends to change when travelling from one medium to another.
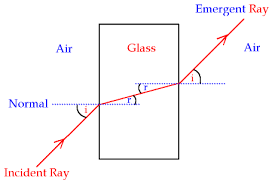
Figure showing refraction of light as it passes from air to glass.
The Angle of Incidence and Angle of Refraction
Measure the angle of incidence and angle of refraction
The angle of incidence (i)is the angle between the incident ray of light and the normal at the point of incidence.
The angle of Refraction (r)is the angle between the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence.
The Laws of Refraction
State the laws of refraction
First law of refraction
The First Law of refraction states that "the incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incident are located in the same plane.”
Second law of refraction
Second Law of refraction states that “when a light ray passes from one medium into another medium, the angle of incidence (i) and corresponding angle of refraction( r) are such that the ratio of sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction (sini/sinr) is a constant value called the refractive index."
Note: The Second Law of Refraction is called Snell's Law in honour of a Dutch scientist named Snell (1591 – 1626) who first described it.
The Refraction Index of a Material
Determine the refraction index of a material
Refractive index (n) is the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction.
n = Sini/Sinr OR
Refractive index (n) is the ratio of the velocity of light in air to the velocity of light in glass.
n = Velocity of light in air (Va)/Velocity of light in glass (Vg)
Or
Refractive index, n is the constant number which expresses how many times or to what extent a light ray bends when passing through different medium.
Absolute refractive index (na) is the refractive index between vacuum or air and any other medium.
The refractive indices between air and some common media is given below:
| Medium | Refractive index (n) |
| Diamond | 2.417 |
| Ethanol | 1.360 |
| Glass (Crown) | 1.520 |
| Quartz | 1.553 |
| Water (at 20ºC0 | 1.333 |
| Air (at stp) | 1.00029 |
Example 2
The refractive index for light passing from air to water is equal to 1.333 find the refractive index for light travelling from water to air.
Data given:
Refractive index anw of air to water = 1.333
Required: To find refractive index from water to air
Since
anw = 1.333
wna = (1/anw)
= (i/1.333)
: wna = 0.75
Real and Apparent Depth
Real depthis the actual height measured without taking account any refraction of light
Apparent depth is the virtual height measured when viewed by observer.
The Concept of Critical Angle and Total Internal Reflection of Light
Explain the concept of critical angle and total internal reflection of light
Critical angle
Critical angleis the angle of incidence (i) for which the angle of refraction (r) is equal to 90º . It is obtained when light rays moves from a dense medium to a less dense medium.
For refractive index
n=Sini/sinr
But i= Critical angle, C
r = 90º
Thus n= sinC/sin 90º
n=SinC/1
n = Sin C
c= Sin -1 (n)
Total Internal Refraction
This occurs when a light ray from a less dense medium is reflected into the denser medium at the boundary separating the two media.
Conditions for total internal reflection to occur include the following:
- Light must be travelling from a more dense to less dense medium.
- Light must incident at the boundary at an angle greater than the critical angle (C).
Optical fibres
These are very thin tubes of plastic or glass and because they are so thin they can bend without breaking, so they can carry light around the corners.
Uses of optical fibres
- Used in telecommunications to carry telephone calls over vast distance, without loss of intensity and without interference.
- Used in endoscope to view inside a patient body for example inside stomach. Light is carried into the stomach through a bunch of fibres and is reflected into small camera, which then displays a picture on a screen.
The Occurance of Mirage
Explain the occurrence of mirage
This is the phenomenon inwhich an object appears to be at an incorrect position due to the bending of light rays from the object.
Mirages occur during hot days.















0 comments:
Post a Comment