Refraction of Light by Rectangular Prism
The Passage of Light through a Triangular Prism
Trace the passage of light through a triangular prism
Deviation of light in a prism is the changing in direction of the incident ray when it enters/hits a triangular glass prism.
Where i
is the angle of incidence
s is the angle of deviation
The minimum angle of deviation ( qm)
In order to determine the minimum angle deviating (Qm) then we must set triangular Glass prism as follows.
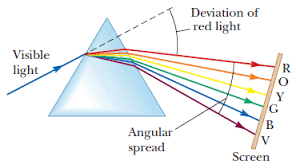
The Dispersion of White Light
Demonstrate the dispersion of white light
Dispersion of light is the splitting up of light beam (white light) into its seven components of colour by a prism.
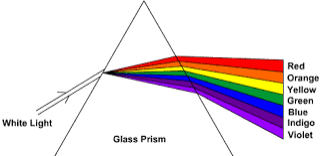
Spectrum is the patch or band of colours which comprise / constitute seven component of white light.
Pure section is the patch or band of colours in which the colours are clearly separated.
In order to produce pure spectrum then we must use two converging lenses (convex lenses).
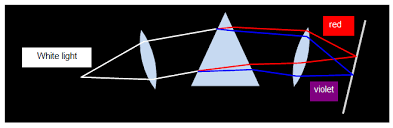
When colours of spectrum are combined, they form white light.
In order to combine colours of the spectrum, weneed two triangular glass prisms and one lens.
Impure spectrum:the band/patch of colours which overlap and are not seen clearly.
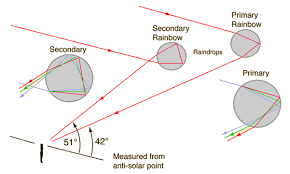
The rainbow:a bow-shaped spectrum of seven colours of white light formed when white light undergoes dispersion within the rain drops because water is denser than air, so has a large refractive index.
Activity 1
A rainbow can be demonstrated as follows:
Spray some water into the air in a direction opposite to that of the sun.
Look at the water shower while you face away from the sun. You will see the colour of the spectrum of white light in the falling drops of water. The spectrum so formed hasthe shape like a bow. So it is called rainbow.
There are two main types of rainbow:
- Primary rainbow
- Secondary rainbow
Primary rainbow
This is formed when light undergoes one or single total internal reflection in the water droplets. In this type of the rainbow the violet colour is on the inside of the bow while the red colour is on the outside.
The Angles of Deviation and Minimum Deviation
Determine the angles of deviation and minimum deviation
Finding the refractive index (n) of glass by using the deviation of light in a prism:
Refracting angle of prism is A
Snell’s law
S in i/Sin r = N
Sin i= n sin r
Sin e’ = nsin i
From Geometry of figure
I = A- r
The total angle of deviation (s) is the angle between the direction orf the incident ray and the emergent ray.
Again from the Geometry Q is given by:
S= i+r’- A
When the deviation is a minimum (Sm) the passage of light through the prism will be symmetrical so:
I = r ‘and r = I’
This means that;
A + Smin = 2i = 2r’
Therefore;
Refractive index, n = Sin (A + Smin)/2
Sin (A/2)
Where
A = Apex angle ( angle of prism)
Smin – The angle of minimum deviation
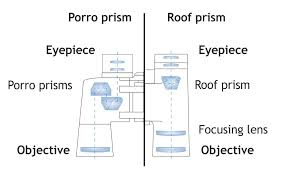
A Simple Prism Binocular
Construct a simple prism binocular
Simple prism binocular















well prepared notes
ReplyDelete