Colours of Light
The Component of White Light
Explain the component of white light
There are two types of colour of light
- Primary colour of light
- Secondary colour of light
Primary colour of light
These are basic (fundamental ) Colour of light to which the eye is most sensitive.Primary Colour of light Include the following
- Red
- Green
- Blue
Secondary colours of light
These are colour of light obtained after mixing primary colours of light
Colour mixing by Addition
This is the process of combining primary colours of light without loss any colour to form secondary colours of light.
| Primary color | Secondary color | |
| Red + Blue | Magenta | |
| Red + Green | Yellow | |
| Blue + Green | Cyan |
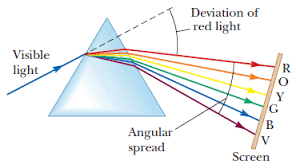
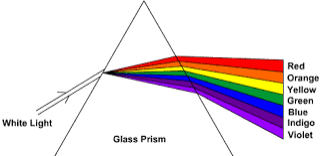
Colours of White Light
Recombine colours of white light
When all white light ( Red , Blue and Green)Combineforms WHITE LIGHT.
Complementary colours of light: These are the colours which produce white light when combined.
- Red + Blue+ Green - White light
- Red + Cyan - White light
- Blue + Yellow - White light
- Green + Magenta - White light
The Appearances of Coloured Object under White Light
Explain the appearances of coloured object under white light
There are two types of coloured paints ( pigments) which Include the following
- Primary coloured pigment (paints)
- Secondary coloured pigment (paints)
Primary, Secondary and Complementary Colours of Light
Identify primary, secondary and complementary colours of light
Primary Coloured pigments
These are basic coloured pigments which form secondary coloured pigment when combined.
The primary coloured pigments include:Yellow, Cyan and Magenta
Secondary colour pigments
These are coloured pigments which are formed when two primary colours combine, whichis always accompanied with the removal of other colours.
Difference between Additive and Subtractive Combination of Colours
Distinguish between additive and subtractive combination of colours
Colour Mixing by Substration
Is the process of mixing two primary coloured paints ( pigments) to form secondary colour white.
Example 3
- Magenta + Cyan
- Magenta = ( Blue) + ( Red)
- Cyan = (Blue) + (green)
The colour which is common to Blue will appear while red and green disappear.
Magenta + Cyan = Blue
Example 4
- Magenta + yellow
- Magenta = (Blue) + (Red)
- Yellow = (Green) + (Red)
The colour which is common to both red will appear while blue and green will disappear.
Hence
Magenta + Yellow = Red
Example 5
- Cyan + yellow
- Cyan = (Blue) + (Green)
- Yellow = (Red) + (Green)
The colour which is common to both green will appearwhile Blue and Red will disappear
Hence
Cyan + Yellow = Green