Density and Relative Density
The Concept of Density of a Substance and its S.I Unit
Explain the concept of density of a substance and its S.I unit
The Density of a substance is its mass per unit volume.
The unit of density is kg/mˆ3. Other unit used is g/cmˆ3.Density of regular solid object can easily be found by direct and easy measurements.-It involves measuring the mass and calculating the volume as described in the experiment below.
The Density of Regular and Irregular Solids
Determine the density of regular and irregular solids
Activity 2
Experiment
Aim;To measure the density of rectangular block.
Material and Apparatus :Ruler, beam balance and rectangular block.
Procedures:Using a beam balance measure mass of the block, m.Measure its length, width and height.
Results
- The mass of the rectangular block is m.
- The volume of the rectangular block will be calculated by multiplying the obtained length, l height, h and width, w.
- Volume, V = l x h x w, But; Density = mass/volume
- The volume of a material can be obtained by using various methods depending on the shape of the material
Activity 3
Experiment.
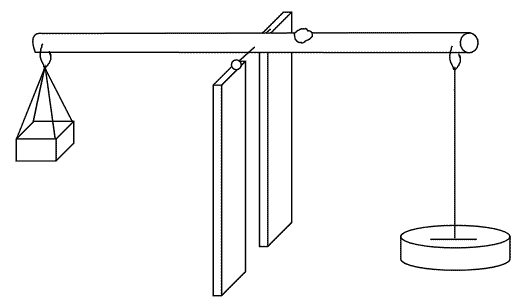
Aim; To determine density of irregular solid.
Materials and apparatus:Irregular solid like stone, measuring cylinder, beam balance and water.
Procedures
- Obtain the mass of the given object using the beam balance.
- Fill water to the measuring cylinder to the volume V₁.
- Immerse the well tied irregular object totally in the cylinder containing water.
- Record the new volume V₂.
Results
- Volume of irregular object = V₂ - V₁
- Mass obtained = M
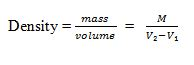
The Density of a Liquid
Determine the density of a liquid
Density of liquids can be determined by using a burrete or a density.
Activity 4
Experiment.
Aim: To determine density of liquids using a burette.
Materials and apparatus: Burette, beaker, beam balance and kerosene.
Procedures
- Record the mass of the empty beaker m₁ using a beam balance.
- Pour the known volume of kerosene into the beaker by using bur rete, V.
- Record the mass of the beaker and kerosene m₂.
Results

Definition of the Relative Density of a Substance
Define the relative density of a substance
The Relative density of a substance is the ratio of its density to the density of water.The density of water has the density of approximately 1.0g/cm³ or 1000kg/m³.
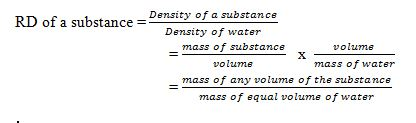
Note:Since the density of pure water is 1g/cm³, the RD of a substance will be represented by the same number as its density in g/cm³.RD has no units as its ratio of same quantities.
Applications of Density and Relative Density in Real Life
Interpret applications of density and relative density in real life
Application of RD in real life.
- It is the key factor which is considered during the design of various structures and equipment. Eg. ships and planes.
- Density is considered during the selection of materials.
- Density is also considered during the design of equipment used in swimming.